Settlement Transducer
KLA-A Settlement Transducer
NKLA-B TML-NET type Settlement Transducer 100 mm to 200 mm
This is a settlement gauge that is set on a ground surface to measure the settlement of each ground layer. Special anchors are placed at target positions in a borehole, and the displacement between the anchors and the ground surface is measured. Measurement can be made at a maximum of six levels in one borehole.
* For information on network-capable NKLA-B, see special measurement systems.
Protection ratings : IP 45 equivalent

- Features
- Remote measurement
- Measures the amount of settlement at the maximum 6 positions.
-
Specifications
Type No. of measurement Capacity Rated output Non-linearity Temperature range KLA-100A-○ 1 to 6 100 mm Approx. 2.5 mV/V
(5000 x 10-6 strain)1 %RO -20 to +60 ℃
(no incing)KLA-200A-○ 200 mm Type No. of measurement Capacity Rated indication Non-linearity Temperature range NKLA-100B-○ 1 to 6 100 mm Approx. 5000 digit 1 %RO -20 to +60 ℃
(no incing)NKLA-200B-○ 200 mm * “◯” under “Type” corresponds to the number of measurements, 1 to 6.
Output polarity
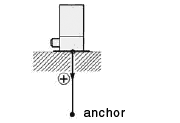
Measurement moves in the plus direction with regard to an increase in settlement.
More Information
Stratified Settlement Meter KLC-50B 50mm
The previous model was installed in a fixed initial position and released using a release wire.
However, it was not possible to confirm whether the fixation was released, and there was a possibility that it remained fixed.
This time, the fixing mechanism was eliminated and the method was changed to adjust the initial position while pulling up the main body of the KLC.
After installation, the sensor's movable part and the grout were completely disconnected to ensure that the ground behavior could be accurately captured.
- Features
- Excellent waterproof property. (Equivalent to IP68)
- No need to replace the meter when excavating the ground.
- No risk of instrument damage during construction.
- Can be installed in borehole φ86.
- Can measure any section displacement in a borehole.
- Maximum number of instruments to be installed: 6
-
Specifications
Model name Capacity Rated output Non Linearity Allowable Temperature Range Weight KLC-50B 50(-20 to +30)mm Approx. 2000 x 10-6 strain 1%RO -20 to +80℃ Approx. 3.8kg *Hydraulic anchors (two-stage type) with enhanced anchorage strength to the ground are also available.
*Please contact us for delivery date.


